Types of Germs
Understanding different types of microorganisms and how to protect yourself from harmful pathogens
BACTERIA
are single-celled microorganisms similar tiny what is microscopic all harmless are harmful... organisms what can cause serious infections, and some can even be life-threatening.
- • Urinary tract infections
- • Throat infections
- • Food and skin ones
- • Sepsis
Treatment: Bacterial infections are typically treated with antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider.
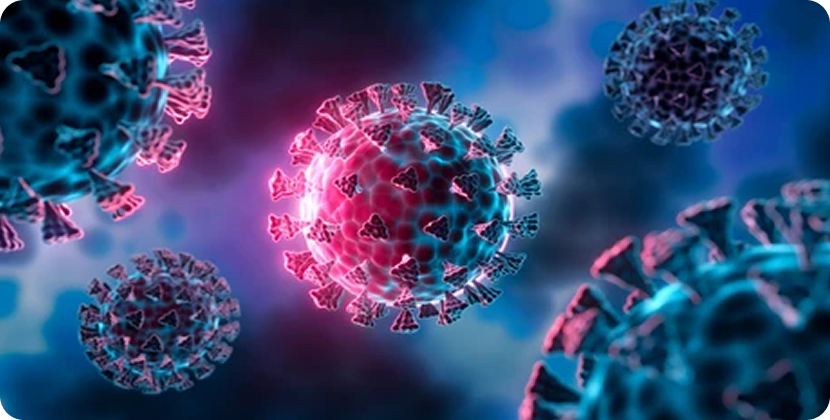

VIRUSES
are much smaller than bacteria and aren't even complete cells. They consist of genetic material enclosed in a protein coat and need a living host like a human body to reproduce. Once they infect a cell, they multiply and spread throughout the body.
- • Common cold, flu
- • Hepatitis
- • HIV/AIDS
- • COVID-19
Treatment: Vaccines are our effective against viruses. Some viral infections may be treated with antiviral medications.
FUNGI
are multi-celled plant-like organisms that thrive in warm, moist and humid conditions for food molds, yeasts, and mushrooms are fungal infections may include:
- • Athlete's foot
- • Ringworm
- • Yeast infections
In people with weakened immune systems, fungi can cause serious infections.
Treatment: Fungal infections are treated with antifungal medications.
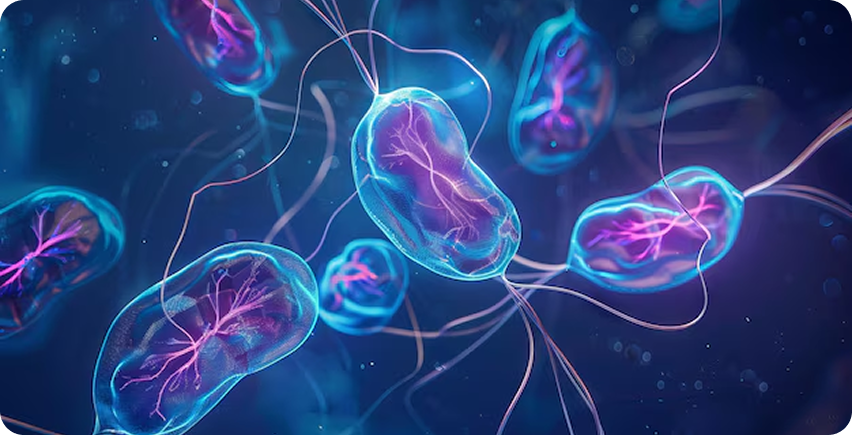
PROTOZOA
are single-celled organisms larger than bacteria. Some live freely in the environment, while others are parasitic, depending on a host to survive. They usually spread through contaminated water, food, or by insects like mosquitoes. These include:
- • Malaria
- • Giardiasis
Treatment: Parasitic protozoa are typically treated with anti-parasitic medications.
HOW DO GERMS SPREAD?
Germs can be transmitted through several common pathways:
- • Direct contact: touching, kissing, or sharing utensils
- • Airborne transmission: via droplets or aerosols
- • Contaminated surfaces: door handles or countertops
- • Food and water: that doesn't change or poor hand hygiene
- • Vector-borne: through insects like mosquitoes, ticks, or flies
Other sources of infection include:
- • Mother-to-child transmission during birth
- • Insect or animal bites
- • Blood transfusions from infected blood or water
How to Protect Yourself from Germs
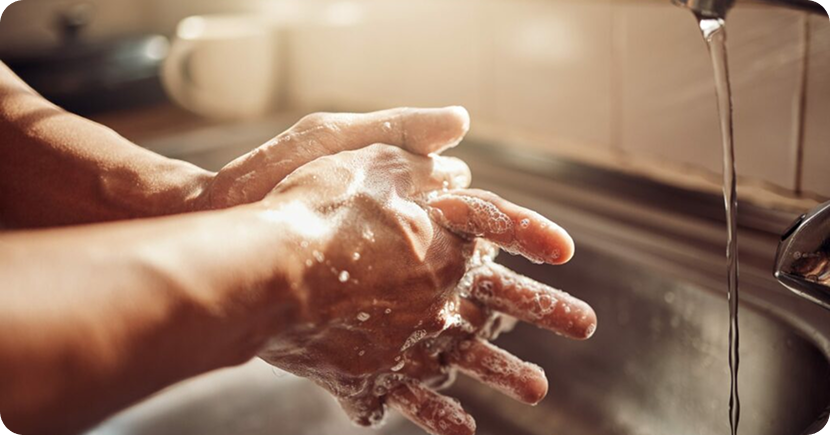
HAND HYGIENE
WASH YOUR HANDS: HAND WASH with water for at least 20 seconds, especially:
- • Before eating or preparing food
- • After using the bathroom
- • After sneezing, coughing, or blowing your nose
When soap isn't available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer like MY CARE+ Gel based 70% Ethyl alcohol moisturizing hand sanitizer!

VACCINATION
Vaccines offer strong protection against specific infectious diseases. Most viral vaccines are given during childhood, adults should also stay up-to-date with vaccines for:
- • Tetanus
- • Influenza
- • COVID-19
- • Hepatitis A
- • Pneumonia and other infections
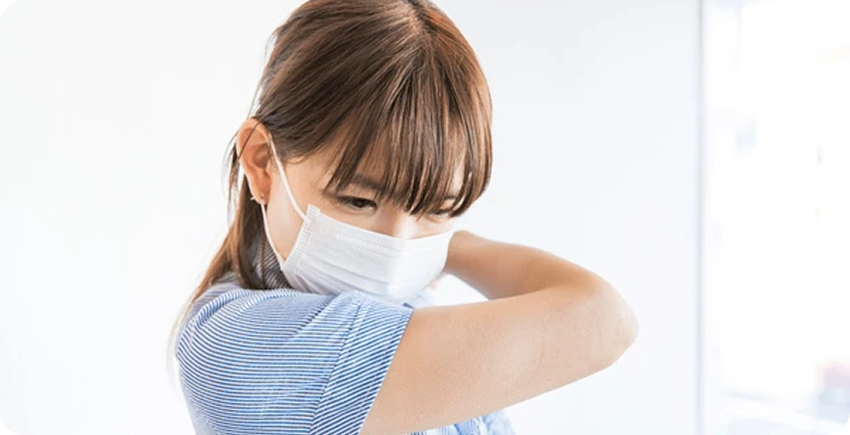
Respiratory Etiquette
- • Cough or sneeze into your elbow
- • Use tissues to handle nasal and dispose of them properly
- • Avoid close contact with others when sick


DISINFECTION & SANITATION
Regularly disinfect high-touch surfaces with trusted products like MY CARE+ Saffron Disinfectant Spray to reduce the spread of germs in your environment.
Healthy Lifestyle
- • Eat a balanced diet
- • Stay active
- • Get enough sleep
- • Maintain personal hygiene
A strong immune system is your first defense against infection.

CONCLUSION
Germs are tiny but powerful organisms that can impact our health significantly. By understanding the types of germs and how they spread, we can take proactive steps to protect ourselves and our loved ones. Simple practices like proper hand hygiene, vaccination, and using trusted products like SAFFROL+ Antiseptic Disinfectant liquid MY CARE+ Gel hand sanitizer & MY CARE+ Disinfectant advance surface cleaners can help keep you and your family safe and healthy.
